As an aspiring pilot, on often comes across a term called “flight computer”. Once a pilot starts the flight training journey this might be a tool one would use on daily basis but for an aspiring pilot, it might sound like a little confusing. So, what is a flight computer and how does a pilot use it?
A flight computer is a versatile tool that enables pilots to perform various complex calculations required for navigation, fuel management, and wind correction. It is typically a circular slide rule device, although more modern versions are electronic, featuring a variety of functions and data important for flight planning and in-flight tasks.
Despite the advent of advanced GPS and digital technology, flight computers remain a staple in pilot training and flight examination due to their reliability and independence from electrical power. Unlike the sound of the tool, it does not look anywhere similar to what a modern computer looks like.
Let’s start by understanding how a pilot uses a flight computer in flying.
How does a pilot utilize a flight computer in flying?
During pre-flight planning, a pilot utilizes the flight computer for various computations like calculating fuel burn, wind correction, time en route, and true airspeed. The pilot enters known values into the computer, such as wind speed and direction, planned airspeed, and course, and the computer then provides the adjusted calculations.
This detailed planning is done to ensure that the aircraft has enough fuel for the journey and that the estimated arrival time and course are accurate.
In-flight, the use of a flight computer evolves to more dynamic applications. It becomes a tool for real-time problem-solving and decision making. Pilots use it to continually update their flight plan based on actual flight conditions, recalculating fuel burn and time en route, or even determining a new course if the planned route is no longer viable.
It also helps in calculating the rate of descent and the time it will take to reach a lower altitude. Thus, while the flight computer serves as a planning tool on the ground, it turns into a critical navigation and problem-solving aid in the air.
For a quick demo of how a flight computer shows valuable data for pilot, check out this online tool by E6BX
History of Flight Computers in Aviation
The genesis of flight computers dates back to the early 20th century. During the era of open-cockpit biplanes, pilots needed a simple and reliable tool to help them navigate. The E6B flight computer, invented by Naval Lieutenant Philip Dalton in the 1930s, was the answer. Made of two circular slide rule discs and a transparent rotating azimuth, the E6B was hailed for its ability to provide crucial flight metrics quickly and accurately.
With the advent of the jet age and the exponential increase in flight speeds and complexity, the mechanical flight computer evolved into the electronic flight computer. The early models, introduced in the 1960s, were relatively basic, providing calculations on speed, altitude, and heading.
However, as technology advanced, so did the capabilities of these electronic aids. Modern flight computers can process and display a wealth of information, including detailed moving maps, flight plans, aircraft systems status, weather information, and much more. Despite these advancements, the fundamental principles of flight computation remain unchanged, and pilots are still trained in the use of the traditional E6B, a testament to its enduring value in aviation.
Overview of components in a E6B flight computer?
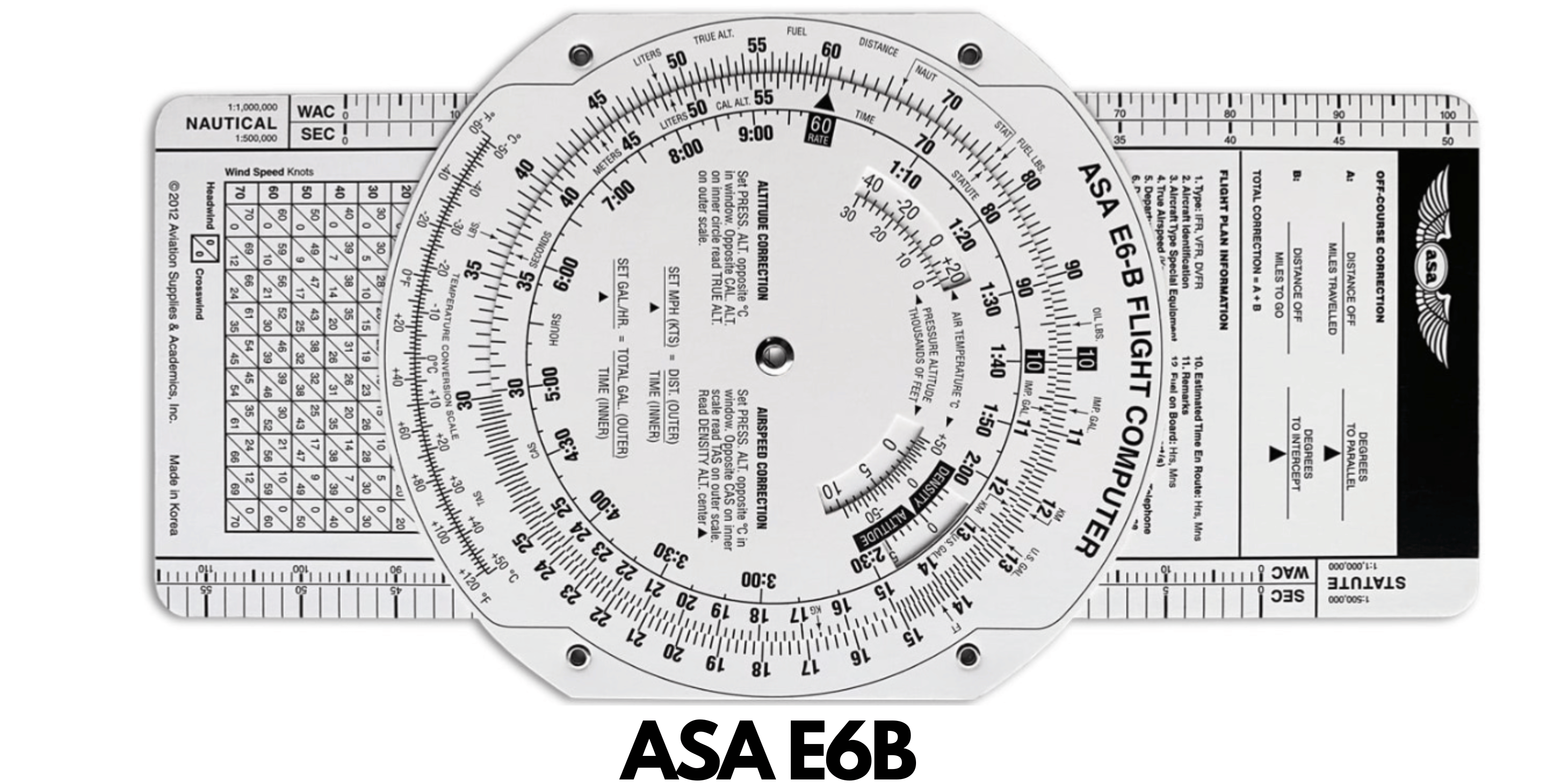
The E6B flight computer, a circular slide rule device, boasts two main parts: the slide and the circular face.
The slide, or the ‘computer’ side, is essentially a mechanical calculator. It facilitates basic math calculations and conversions, fuel consumption computations, time-speed-distance calculations, and wind correction angle determination.
On the reverse side, you’ll find the circular ‘wind’ side. This side assists pilots in visualizing the effects of wind on their flight path and helps in making appropriate corrections. It’s divided into a semi-transparent rotating azimuth for wind computation and a circular slide rule for quick multiplication and division.
Using an E6B flight computer requires an understanding of these components, along with a good grasp of the principles of flight planning and wind correction. Despite the complexity, its robust utility makes it a staple in pilot training even today.
What are the different types of flight computers used in aviation today?
Today, aviation utilizes a variety of flight computers that range from the traditional E6B to advanced electronic flight computers.
Mechanical Flight Computer
Also known as an E6B, this is a manual flight computer that utilizes slide rule and circular slide rule calculations. It’s most often used in flight training to help new pilots learn the basics of flight computations, including calculating fuel burn, wind correction, time en route, and conversions.
However, its usage is limited in more complex or high-stakes scenarios due to the advent of digital flight computers.
Handheld Flight Computer
This type of flight computer is portable and electronic, designed to offer more convenience and accuracy than mechanical flight computers. It is most commonly used during shorter flights where quick calculations are needed, without the need for constant updates.
Tablet-Based Flight Computer
As the name suggests, this type of flight computer is software-based and can be used on tablets or smartphones. It is more versatile and feature-rich, allowing pilots to access weather updates, charts, and flight preview tools. It’s ideal for longer, complex flights that require comprehensive planning and real-time updates.
Aircraft Integrated Flight Computer
This is the most advanced type of flight computer, directly integrated into an aircraft’s avionics system. It offers the highest level of integration and data accuracy. Usually used in commercial and military aviation, it’s designed for high-stakes, precision-based scenarios that necessitate real-time data and enhanced safety measures.
What are the best Mechanical Flight Computers used in aviation
ASA E6-B Metal Flight Computer
It is one of the most popular mechanical flight computers used in aviation. This device offers a variety of features such as wind triangle, time-speed-distance calculations and fuel consumption calculations. It also has a slide rule with three scales so pilots can easily calculate their desired results.
Popular for: High among aviation professionals and trainees for its durability and precision.
Pros: Additional features like the ability to calculate drift, ground speed, track to compensate for wind.
Cons: Some users find it slightly more complicated than other models.
CR-3 Flight Computer
The CR-3 Flight Computer is distinctively designed with features like a built-in protractor and hemispherical wind triangle. It also has an aircraft performance calculator, which is useful for pilots who need to calculate the takeoff speed and climb rate of their planes.
Popular for: Preferred for those seeking portability due to its compact size.
Pros: Small, compact, and capable of various aviation calculations.
Cons: The smaller fonts and scales can be challenging to read and use.
APR E6-B2 Flight Computer
The APR E6-B2 Flight Computer is a specialized device with large, easy to read scales for accurate computations. It includes an aircraft performance calculator and offers the ability to calculate wind correction angles and ground speed.
Popular for: Gaining popularity for its modern features and added functionality.
Pros: It comes with color-coded conversion scales and a wind component grid.
Cons: More expensive compared to other traditional models.
Jeppesen Student CSG Computer (Slide Graphic Computer)
The Jeppesen Student CSG Computer is an all-in-one flight computer designed for students. It includes multiple scales and can be used to calculate wind correction angles, time/speed/distance, fuel consumption rates, and much more.
Popular for: Very popular among student pilots for its simplicity.
Pros: Emphasizes simplicity and ease of use along with basic calculation functionalities.
Cons: Might lack some of the advanced features that other computers offer.
What are the best Handheld Flight Computers used in aviation
Sporty’s Electronic E6B Flight Computer
The Sporty’s Electronic E6B Flight Computer is a digital flight computer that replicates the traditional mechanical paper slide rule. It features a full-color LCD screen, along with an aircraft per- formance calculator, which is useful for pilots who need to calculate the takeoff speed and climb rate of their planes.
Popular for: Highly popular in the aviation community for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive features.
Pros: Offers a wide range of aviation functions, from basic arithmetic to complex flight planning calculations. It is easy to use and highly accurate.
Cons: Some users may find it a bit pricey compared to mechanical models.
ASA CX-3 Flight Computer
The ASA CX-3 Flight Computer is a lightweight and compact flight computer that fits easily into any pocket. It features easy-to-read scales, a built-in calculator, and an adjustable leg for precise measurements.
Popular for: Loved by professional pilots for its advanced features and reliable performance.
Pros: Features an intuitive menu and keyboard, generous display, and a multitude of functions covering all aspects of flight.
Cons: Its complexity may prove daunting for beginners.
Gleim E6B Flight Computer
The Gleim E6B Flight Computer is an affordable and reliable aviation computer. It is designed to be used in conjunction with the Gleim Pilot Logbook, allowing pilots to calculate and record their flight times instantly.
Popular for: Favored by student pilots for its simplicity and affordability.
Pros: Provides all the necessary functions for flight school and beyond. It’s durable, easy to read, and reasonably priced.
Cons: Does not include some of the more advanced features found on pricier models.
What are the best Tablet-Based Flight Computer applications used in aviation
ForeFlight Mobile
ForeFlight Mobile is a comprehensive flight planning and execution app for Android and iOS devices. It offers powerful features such as high-definition weather, real-time forecast tracking, 3D navigation maps, aviation documents storage and management, data logging capabilities, and more.
Popular for: ForeFlight is highly favored by pilots due to its comprehensive set of features and seamless integration with onboard systems.
Pros: It offers a plethora of functions such as flight planning, weather briefing, traffic awareness, and 3D preview. It also provides synthetic vision, electronic charts, and logbook features.
Cons: Subscription to ForeFlight is expensive, and the vast array of features can be overwhelming for new users.
Garmin Pilot
Garmin Pilot is an app developed specifically for Android and iOS devices. It provides a versatile suite of features including flight tracking, weather briefing, 3D navigation maps, and more.
Popular for: Garmin Pilot is admired by many pilots for its advanced navigation features and compatibility with Garmin avionics.
Pros: It provides interactive mapping, flight planning, 3D Vision, and weather data. It also supports split-screen views and can integrate with a wide variety of Garmin hardware.
Cons: Some users have reported occasional software glitches, and it may require additional hardware for optimal use.
FltPlan Go
FltPlan Go is an app designed for Android and iOS devices. It includes a full suite of features such as flight tracking, weather briefing, 3D navigation maps, aviation documents storage and management, data logging capabilities, and more.
Popular for: FltPlan Go is a popular choice for its affordability and comprehensive feature set.
Pros: It offers features like moving maps, approach charts, and in-flight weather information. It also has airport information, fuel prices, and navigation logs.
Cons: Its user interface is not as polished as some of its competitors, and it might require a learning curve to fully utilize its features.
Some other frequently asked questions about flight computers
Do pilots still use E6B Flight Computer?
Pilots still use the E6B flight computer, particularly during their training. Known as the “whiz wheel,” the E6B is a traditional, analog flight planning tool that has been used by pilots since World War II. Despite the advent of electronic flight computers and sophisticated avionics, the E6B remains a reliable and versatile tool.
It’s primarily used for planning and estimating flight time, fuel usage, wind correction, and ground speed. While many pilots nowadays may rely more on digital solutions for these calculations, the E6B is still taught in flight schools to ensure pilots have a fundamental understanding of flight planning and navigation principles.
Why is the E6B flight computer called E6B?
The E6B flight computer gets its name from its original part number assigned by its manufacturer, the United States Army Air Forces, during World War II.
The “E” stands for “Equipment,” “6” represents the sixth piece of equipment listed under the “E” category, and “B” signifies the second iteration or revision of the design. Thus, the name “E6B” essentially refers to its place and version in the military equipment inventory.